搜索整个车站
Scope of application
Environmental protection supports research on the regeneration of activated carbon for industrial wastewater treatment (burning out adsorbed organic matter), in-situ activation of VOCs adsorbing carbon fibers, and pore structure optimization of biochar soil conditioners.
A steam-activated tubular furnace is a tubular heating device that uses high-temperature steam as the activation medium. Its operating principle is to generate high-temperature steam (typically ≥800°C) by heating water. This steam is then introduced into the furnace tubes, where it chemically reacts with materials (such as activated carbon and minerals), achieving material activation, modification, or structural reconstruction. At high temperatures, steam acts as an oxidant or reaction medium, modifying the material’s microstructure (e.g., porosity and specific surface area) through etching and pore expansion, thereby enhancing its adsorption properties or catalytic activity.
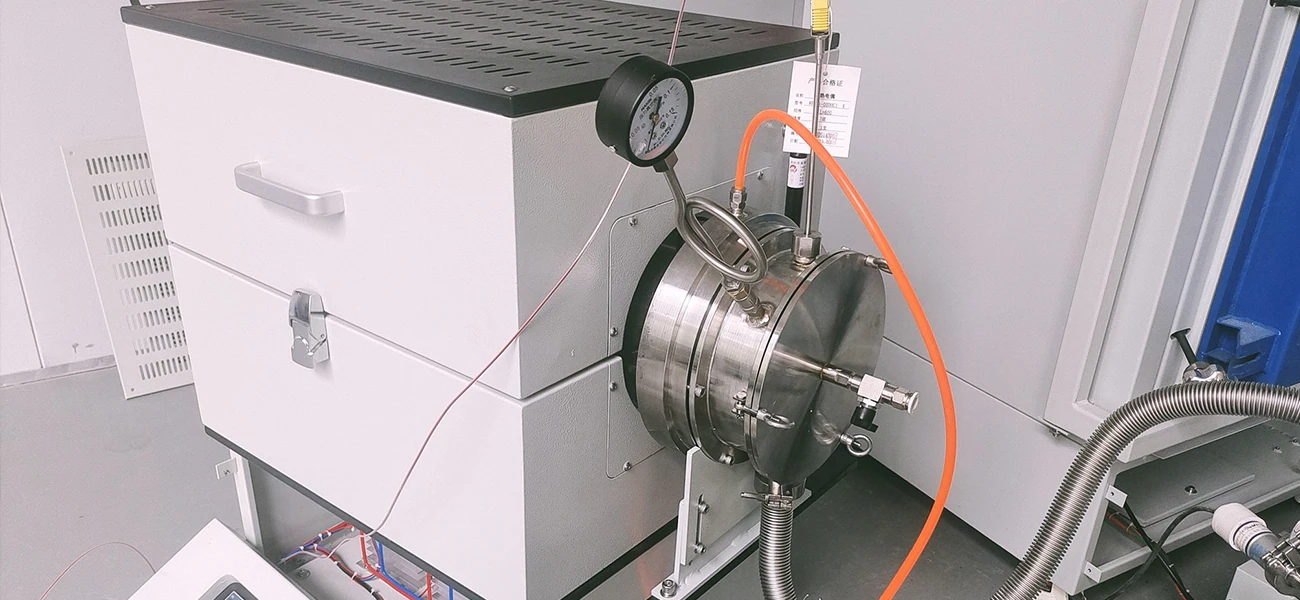
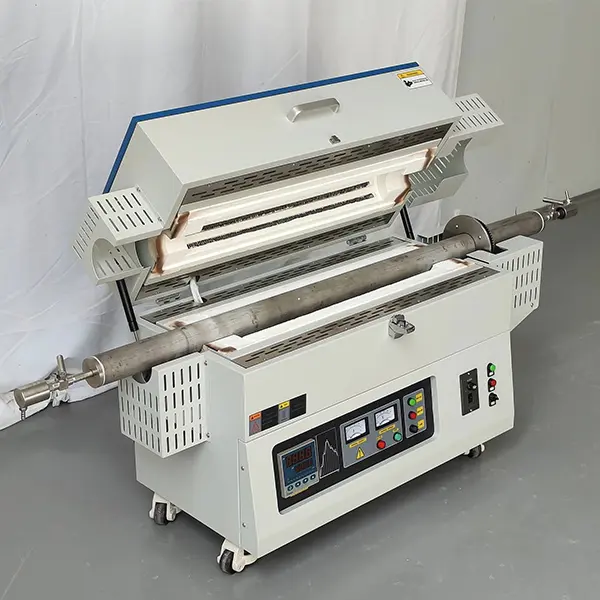
Main Technical Structure and Features
Furnace Tube Design: Furnace tubes are typically constructed of high-temperature resistant materials (such as quartz and corundum). Some devices utilize a multi-tube parallel structure (such as the multi-tube activation furnace described in patent CN202411309450.9). A steam pipe is located in the center of the tubes, evenly distributing steam through high-temperature steam holes to ensure sufficient contact between the material and the steam.
Heating Method: Electric heating is the primary method, with some devices incorporating radiant heating technology. Internal heating elements convert electrical energy into thermal energy, achieving uniform temperature distribution within the tubes with a control accuracy of up to ±1°C. Steam Supply System: A boiler heating assembly is typically installed beneath the furnace body, heating water to high-temperature steam before passing it into the furnace tubes. Steam flow and pressure can be precisely controlled via valves.
Material Transportation: Some industrial equipment utilizes a tilted furnace body or rotating furnace tube design, allowing continuous material inflow through the raw material inlet and out through the bottom outlet after activation, enabling continuous production.
Typical Applications
Activated Carbon Preparation and Regeneration: In the environmental protection and chemical industries, steam activation is a core process in activated carbon production. High-temperature steam etches carbon precursors (such as sawdust and coal) to create a rich porous structure, which is used for wastewater treatment, gas adsorption, and other applications.
Catalyst Activation: In chemical production, steam is used for catalyst activation and regeneration. Steam removes carbon deposits or impurities from the catalyst surface, restoring its active sites and extending its service life.
New Energy Material Processing: In the preparation of battery materials (such as lithium battery cathode materials), steam activation modulates the material’s crystal structure and surface chemistry, improving its ionic conductivity and cyclic stability. Laboratory Research: Suitable for small-scale material activation experiments, such as optimizing the performance of new adsorbent materials and catalytic supports.
Technical Advantages and Development Trends
Advantages: Compared to traditional activation methods (such as chemical activation), steam activation offers a clean process (no chemical reagent residue), high activation efficiency, and high product purity. Its tubular structure facilitates continuous production and precise temperature control.
Trends: With the increasing demand for industrial intelligence, steam activation tubular furnaces are moving towards multi-tube integration (increasing production capacity), intelligent control (such as PLC-linked steam flow and temperature), and energy conservation and environmental protection (waste heat recovery systems). Applications in new energy materials and environmental protection are also expected to expand.
Selection and Considerations
Selection Parameters: Consider the furnace tube inner diameter (affecting processing capacity), maximum operating temperature (typically 800-1200°C), steam pressure range, temperature control accuracy, and atmosphere compatibility (such as support for inert gas protection).
Safety requirements: High-temperature steam poses a risk of scalding, so the equipment must be equipped with a pressure safety valve, over-temperature alarm, and emergency shutdown device; the furnace tube material must be selected based on the activation temperature and the corrosiveness of the material (e.g., corundum tubes are suitable for high-temperature and strong acid environments).
| Model | Max temperature | Heating zone length | Constant temperature zone length | Power and voltage | Furnace tube size | Dimensions |
| YXG-1200-A1 | 1200℃ | 200mm | 60mm | 1.5kW/AC220V | φ30/50*500mm | 800*340*400mm |
| YXG-1200-A2 | 1200℃ | 440mm | 120mm | 3kW/AC220V | φ30/100*1000mm | 1120*480*530mm |
| YXG-1200II-200 | 1200℃ | 200+200mm | 200mm | 3KW/AC220V | φ30/100*1000mm | 1100*420*560mm |
| YXG-120OIII-200 | 1200℃ | 3*200mm | 3*60mm | 4.5KW/AC220V | φ30/100*1000mm | 1400*420*560mm |
| YXG-1400-400 | 1400℃ | 400mm | 120mm | 5kW/AC220V | φ30/100*1000mm | 1200*500*660mm |
| YXG-140OIl-200 | 1400℃ | 200+200mm | 200mm | 5kW/AC220V | φ30/100*1000mm | 1200*500*660mm |
| YXG-1700-290 | 1700℃ | 290mm | 80mm | 6kW/AC220V | φ30/100*1000mm | 1300*640*870mm |
